Fortinet NSE3 Certification | Course Notes
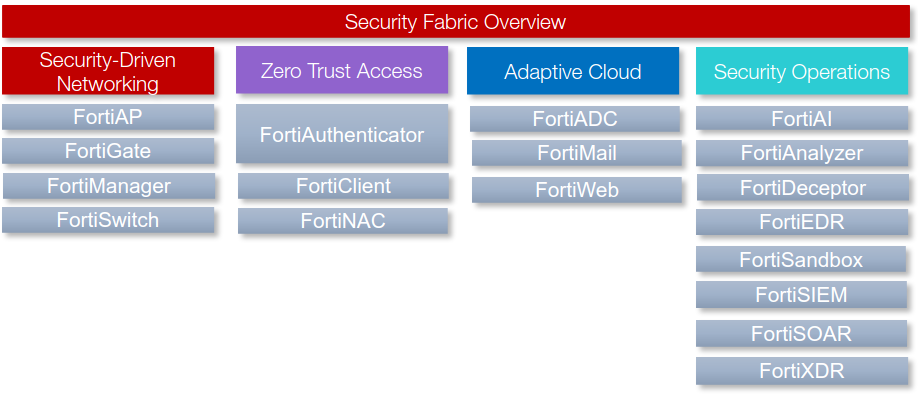
The product lessons and use cases in this course are organized into the following Fortinet Security Fabric pillars:
- Security-Driven Networking
- Zero Trust Access
- Adaptive Cloud Security
- Security Operations
Module 1: Security Fabric Overview
Module Objectives
- Be conversant on the products that comprise the Fortinet Security Fabric, and understand the problems they solve
- Recommend appropriate products to solve organizational network security problems
Why is this course important
This course will help you solve network security problems by understanding the characteristics of the Security Fabric, the capabilities of the products that comprise it, and how they interlock to provide a superior defense against today's most sophisticated cyberattacks.Organizational Problems and Pain Points
- Lack of coordinated threat detection and policy enforcement
- Siloed networking and security
- Security gaps, complexity, and reduced visibility
Trends comes with technology development
- Increasing attack surface
- Rising losses due to sophisticated breaches
- Too many add on products
- More encrypted traffic
Definition
The Fortinet Security Fabric is a platform powered by FortIOS provide a rich open ecosystem to protect device, data, and applicationKey attributes
- Broad: manages the entire digital attack surface (edges, cloud, endpoints, and users)
- Integrated: seals security gaps and decreases complexity providing complete visibility, it also strengthens security in all form factors (Hardware appliances, VMs, Cloud, SaaS)
- Automated: provide faster time to prevention and response using cloud-scale and advanced AI
Security Fabric Pillars:
- Security-Driven Networking
- Zero Trust Acces (ZTA)
- Adaptive Cloud
- Security Operations/Fabric Management Center
 |
 |
Security Fabric Management
- Centralized management
- Network automation and orchestration
- Analytics
Module 2: Security-Driven Networking
Lesson 1: Security-Driven Networking Overview
definition
Security-Driven Networking delivers enterprise protection and user experience at any edge providing secure high-quality performance connectivity between users, applications, and devices;
within an on-premise network and into the cloud, it helps organizations manage internal and external risks using internal segmentation, automated threat protection, and policy enforcement
Digital transformation
Definition
Benefits
- Enhance the collection of data by improving customer experience
- Uses resources more efficiently thus increasing profits, organizational agility, and productivity
Problems:
- Digital transformation creates many network edges (the area where the device or local network interfaces with the internet): mobile devices, IoTs, cloud; which means that the trusted zone as we used to call it is no more trusted
- The security against digital transformation evolved as the situation did, adding new products for each new edge resulting in an inconsistent and complex to manage security
Solution:
Fortinet products across security pillars (like the Security-Driven Networking pillar) work as a team rather than making each pillar work isolated from others thus reducing complexity
Ex: FortiManager is a product that falls under the Fabric Management Center pillar but it contributes to the Security-Driven Networking pillar
Lesson 2: FortiGate
Definition
- FortiGate is Fortinet's NGFW that protect network assets at the edge, in the core, and at the segments of the network
- Powered by FortiOS
- The first FortiGate installed is configured as the root and it is typically located on the network edge

Form Factors
FortiGate is available on the following form factors:
- Physical appliance
- VM (private/public cloud): VMware, Hyper-V, AWS, Azure, KVM, and more
FortiGate scales

Manage FortiGate
you can manage FortiGate using FortiManager as a physical appliance or VM or accessed as a SaaS, which allows you to:
- Centrally manages Security Fabric devices, such as FortiGate, FortiSwitch
- Simplifies device network management
- Provides centralized policy enforcement and provisioning (compliances, legislations, regulations, best practices)
FortiGuard
FortiGate relies on FortiGuard for some security services and threat intelligence (web filtering, security analytics, AI/ML); it ingests and analyzes an average of 100 billion events per day

Lesson 3: FortiAP
Definition
LAN Edge
The FortiAP is part of Fortinet's LAN Edge solution along with FortiGate and FortiSwitch
FortiLink


Management options
from a management perspective, FortiAP has several options for customers as you can see below
FortiWLM

The complexity of network management and operations brings a lot of misconfiguration risk for enterprises, this can be avoided using FortiManager capabilities
Fabric Management Center:
Enables unified network management for all your devices, used by 25k+ clients all over the world, with multiple deployment choices
Fabric Management Center use cases:
- Simplified provisioning: easy deployment, SD-WAN, and NGFW templates, central management console, DevOps playbooks and scripts, config backups with revision history
- Centralized management: Scale to 100k+ FortiGate devices, centralized audit logging, role-based access control
- Network Analytics: network health visibility, real-time SLA reporting, historic SLA reporting, application usage reports and dashboards, an adaptive response handler

- Compliance reporting: PCI DSS compliance reports, FSBP security rating & scoring, customizable regulatory templates, MFA for device consoles, integration with 3rd party SIEM & compliance tools
- Network automation: connectors to SDN and public cloud, ITSM integration with ServiceNow, REST API via fndn.fortinet.com, DevOps tools like Ansible, Puppet, Terraform
Lesson 4: FortiSwitch
Definition
FortiSwitch is a secure switch designed and produced by FortinetDeployment options
Either using FortiLink or as a standalone switchFortinet secure Ethernet through FortiLink

FortiSwitch use cases

FortiSwitch product offerings

Cloud management options for FortiSwitch

Lesson5: Security-Driven Networking use cases
Use case 1: Fortinet Secure SD-WAN

Use case 2: Campus deployment Model through mid-range devices

Use case 3: FortiExtender

Use case 4: FortiExtender Cloud
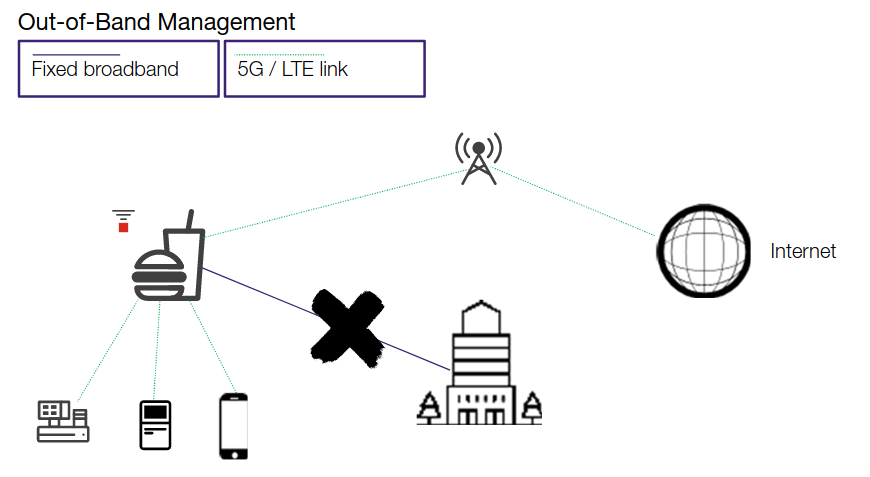
Use case 5: Hyperscale
Hyperscale is the ability of a technology architecture to improve and scale in response to increasing demand on a system, and FortiGate meets those requirements using their SPUsModule 3: Zero-Trust Access
Lesson 1: ZTA overview
Definition
The Zero-Trust Access (ZTA) solution enables organizations to see and control everyone and everything on the network, whether on-premises or off-premises, it ensures consistent security policy use across the network cloud and off the networkTrends and challenges in network access
Remote access, IOTs, and BYOD are new edges to the organization with the internet which present a big concern to the companies' securityWhat problems does ZTA solve?
Inconsistent user experience caused by whether the client's access to resources from in or outside the office:- Access from in or out of the office is identical
- Automatic secure tunnels to applications
- SSO supported
- Hides the applications' locations
ZTA principles
- Authenticate and verify on an ongoing basis
- Give minimal access:
- Segment the network to create zones of control
- Control access to applications, data, resources
- Grant the least privilege access based on need or role
- Assume that the network is already compromised
Reducing the attack surface
- Authenticate user identity per connection
- Supporting strong authentication (MFA and SSO)
- Verifying device identity per session
- verifying device posture per session
- Restricting user access to resources based on need-to-know
- Hiding network applications from the internet (access proxy)
Fortinet ZTA and ZTNA in context
Accessing resources using ZTNA
FortiClient EMS (Enterprise Management Server), it produces Zero Trust tagging rules based on the endpoint properties and sends the rules to the endpoints (used by FortiClient)If an alteration occurred in an endpoint, EMS sends the update to FortiGate to update its policy
ZTA solution products

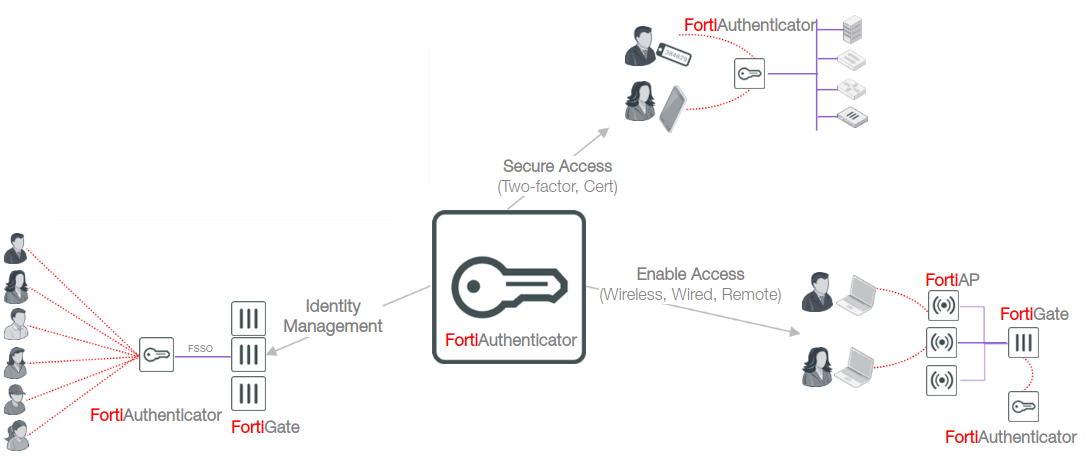
Lesson 2: FortiAuthenticator
Definition
FortiAuthenticator is an identity management product for the enterprise, providing strong authentication and authorization to the connected network
key Feature: Enable access for wired/wireless authentication
- centralized WIFI authentication
- Authenticate users and machines
- Certficate based device authorization for BYOD environments
- 802.1X authentication
key Feature: Enable access for guest management
- User self-registration
- Social authentication (Facebook, Google ...)
- Collection of user details
- Options to SMS login details (proof of identity)
- Time-limited accounts
- Delete expired accounts
key Feature: Secure access by 2 Factor Authentication
- Integration with existing LDAP/Active Directory databases
- Self-service password reset
- Lost token workflow
key Feature: Identity management with SSO
- Defining who can access what and when:
- Collects user identity information
- Granular control of network and application access
- Allows FortiGate, FortiClient, FortiMail, and FortiCache to apply appropriate policy based on user identity and role
- use integrations to capture user identity information:
Lesson 3: FortiClient
Definition
FortiClient is an integrated endpoint agent with a modular design (3 modules > 3 use cases)What problems does it solve
- Lack of visibility
- Vulnerable endpoints
- unsuspecting users
Fabric-Integrated endpoint security
FortiClient connects endpoints with the Security Fabric via FAbric Agent, it delivers:- Endpoint visibility: endpoint telemetry, vulnerability scanning, security posture, software inventory
Lesson 4: FortiNAC
Definition
FortiNAC is the Fortinet network access control product, it's a security solution that identifies and enforces policy on devices that access networks to increase visibility reduce risk, providing visibility, control, and automated response.Key platform differentiators
- Broad device awareness: supports 2.500+ network infrastructure devices and 170+ vendors
- Wired/wireless capabilities: not reliant on 802.1x only, consistent experience
- Scalable architecture: centralization
















Comments
Post a Comment